We have implemented improvements to two-factor authentication. The latest version of Dataprius incorporates these improvements.
This new version is available for download on website: Downloads Dataprius

The two types of two-factor authentication that exist in Dataprius
- Two-factor authentication by sending a code by email.
- Two-factor authentication by Authenticator application code.
On the user’s profile of each user in the system, you can select the type of authentication:
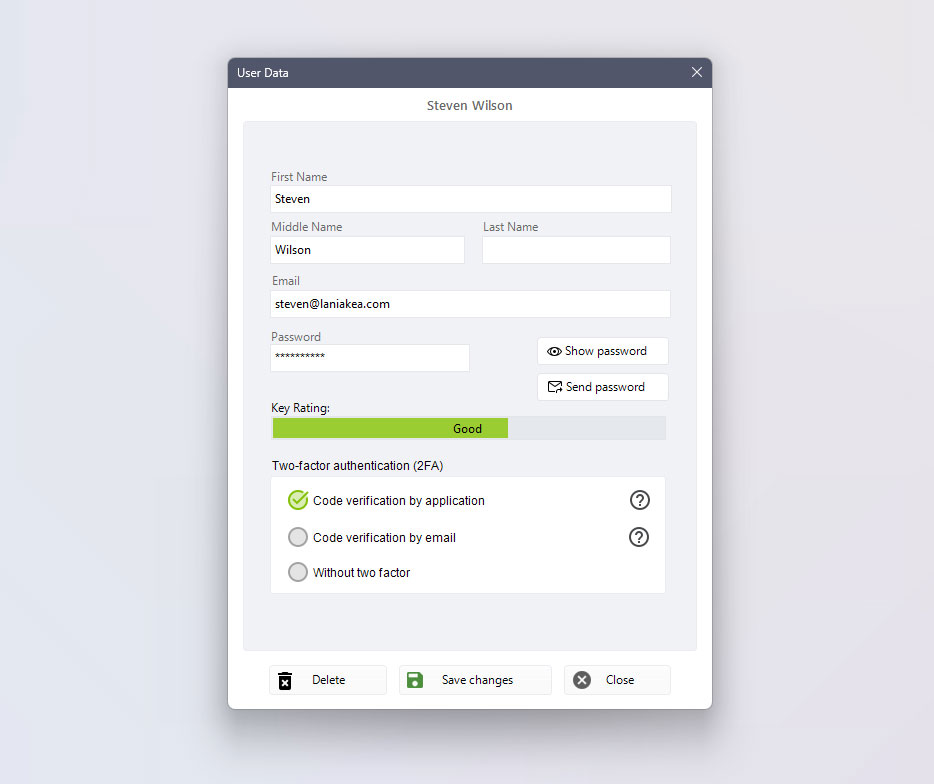
The application displays support for these two types of authentication.
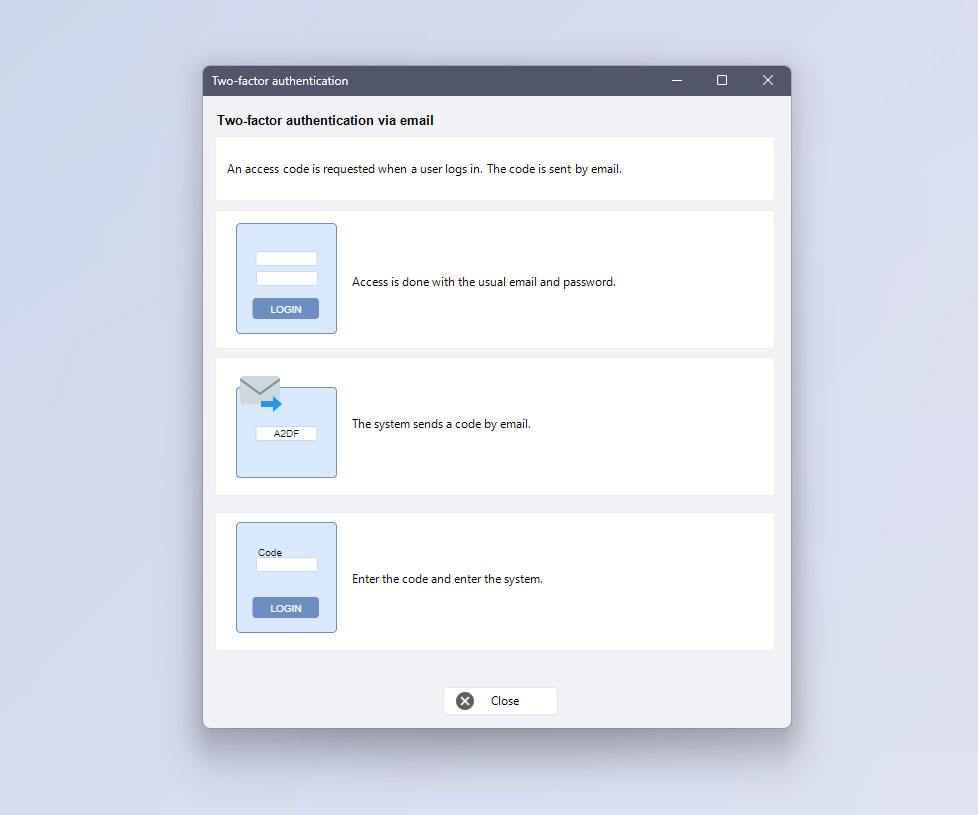
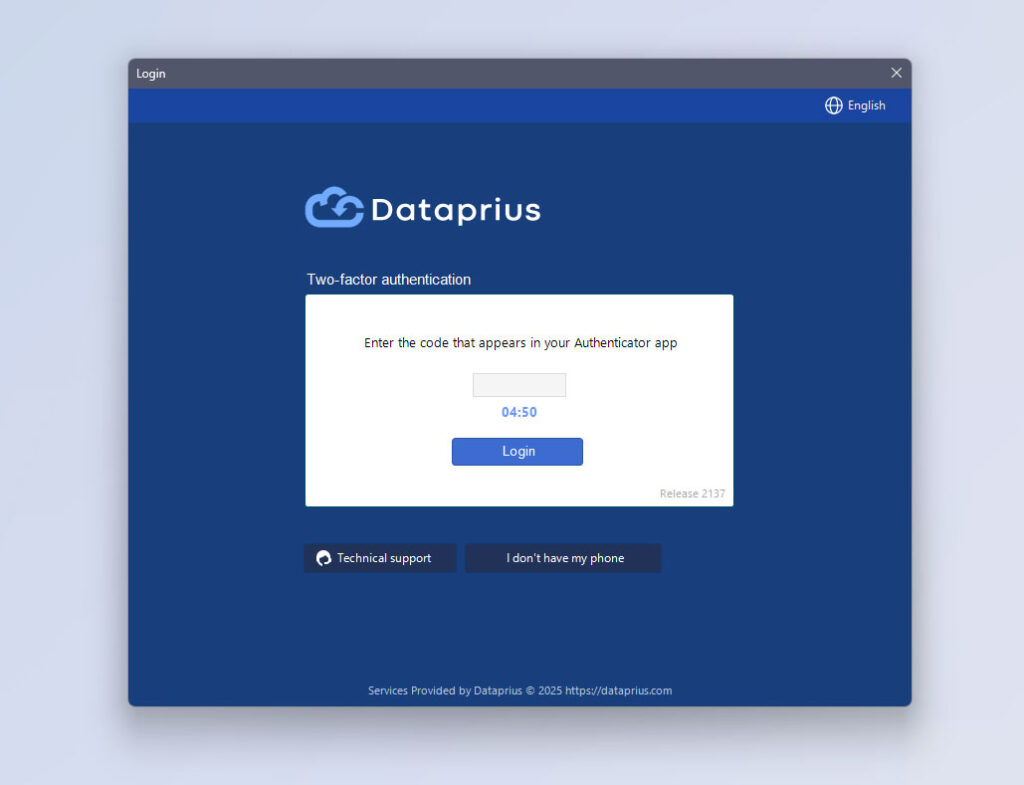
Two-factor authentication by email
- You log in with your email and password in the usual way.
- The system sends a code by email.
- You enter the code and log in.
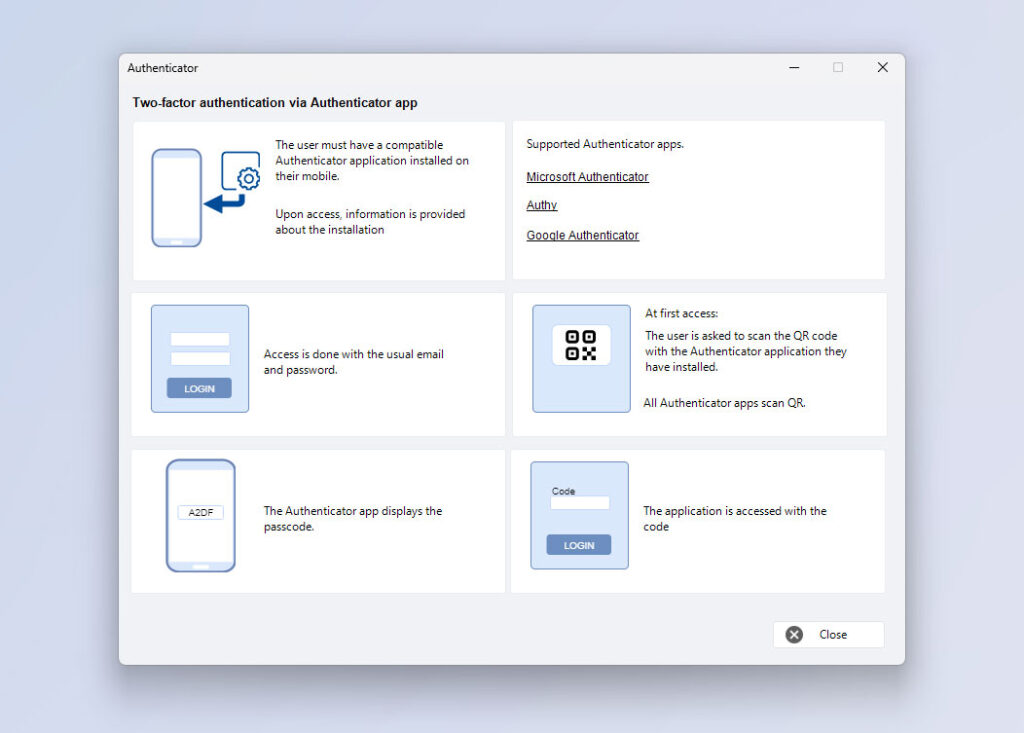
Two-factor using authenticator application
- During the first access.
You are asked to scan the QR code that appears on the screen with the Authenticator application, installed on your mobile phone.
There are several compatible Authenticator applications. They are available for Android and IOS.
- You enter the system by entering the code.
- After the first login, QR scanning is no longer necessary. When the application asks for the code, you will need to enter the code shown by the Authenticator application.
Two-factor access in Dataprius Desktop application
We illustrate with screenshots the steps described above.
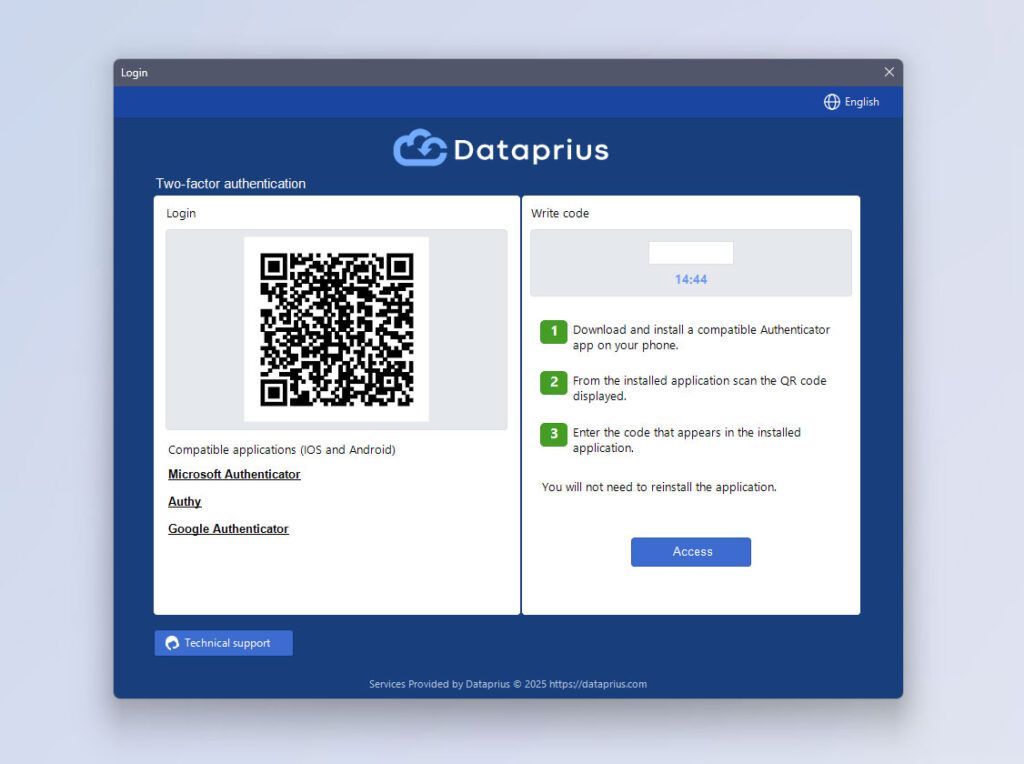
After scanning the QR and entering the code that Authenticator displays on your mobile phone, you will be able to access the system.
From that moment onwards, the application will ask you for the authenticator code every time we enter the system.
General information on two-factor authentication and OTP protocols.
Two-factor authentication (2FA)
Two-step verification, also known as two-factor authentication (2FA), two-factor or similar, is a security measure in addition to the password. It is used to protect online user accounts from unauthorised access.
Generally, two-step verification is performed in two steps:
- First step, enter the first factor: Something the user knows, such as a password or PIN code.
- Second step, provide the second factor: Something the user possesses, such as a mobile device, physical key, USB device, etc… to which a temporary unique code known as OTP (One-Time Password) is sent or allowed to be generated and entered in the login process.
The use of these two factors makes it much more difficult for attackers to gain access to an account, even if they obtain or guess the password. The idea is that if one authentication factor is compromised, which is usually the first one, the other factor is still necessary to access the account.
This way they would not be able to access your user account.
Therefore, it is recommended to enable two-step verification on all online accounts that allow it. Among these we find: email, social networks, instant messaging, online banking services and other services that store sensitive data, such as cloud storage services, marketplaces or online shops. Each service may have its own way of setting up two-step verification, so it is important to follow the specific instructions provided by each platform or service where you want to enable it.
What is OTP and TOTP?
Although the technology behind OTP is complex, the name is self-explanatory – OTP stands for One Time Password. One Time Passwords are security codes that you can use only once to authenticate yourself.
Each OTP is unique and consists of combinations of numbers and, in some cases, letters. This allows for an almost infinite number of random combinations, which makes the OTP security layer more resistant to attack.
We have already established the key principles of OTPs, so let’s get a little more specific and find out what a TOTP is. The second half of the acronym stands for ‘one-time password’, while the T stands for its main feature: ‘time-based, time’.
Basically, time-based one-time passwords are passwords that expire at a predetermined time, known as a timestep. Different TOTP authentication tools use different timesteps, but the validity of a code can range from 15 seconds to one minute.
If you do not type in your unique authentication code during this time period, the password is reset and you have to enter a new code. The time factor is the key aspect of a TOTP’s cybersecurity advantage. Because random passwords change so quickly, they are more difficult to attack.
Source: Nordpass (What is OTP?)


